The only step-by-step guide you need to succeed in SEO

Sales funnels, social media strategies, email marketing…these are only a few of the things any digital entrepreneur has to understand and apply.
As someone who has worked with several digital businesses, I know how overwhelming all of this can feel.
Unfortunately, I can’t provide a solution to all these areas, but after reading this post, you’ll be able to cover one of the essential areas of any digital business: SEO.
Setting up a website is easier than ever before, but how do you ensure people find your work?
SEO is the most effective way so that people really find your website.
You probably read articles on keyword research, backlink strategies, and H1 tags before and you might be aware of the importance of SEO, but how do you put all of this into action?
“A website without SEO is like a car with no gas.”
— Paul Cookson
WordPress.org was the CMS of choice for the websites I created. In retrospect, I can also recommend wordpress.org from an SEO perspective as there are great plugins and resources.
SEO is significant leverage to increase your visibility in the online space.
SEO can help yoga teachers, product owners, company co-founders, dentists, etc. — anyone who owns a website. Important message first: you do not need to have coding skills. Let’s take a deep dive into the three significant areas of SEO.
On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO is everything you do on your website. More specifically, on-page SEO contains Keyword Research, Content Strategy, and SEO Copywriting.
Keyword research
Keyword research is the most important part of On-Page SEO. Unfortunately, I did not take this seriously two years ago and wrote my first blog articles before doing keyword research. By skipping the research step, my pieces were, from an SEO perspective, useless.
Without proper keyword research, you optimize for words that don’t help you advance your business or product. Here’s how to do proper keyword research so that you don’t waste as much time as I did.
First, consider your company’s mission and your audience before diving into the technical part of keyword research.
What is your unique selling proposition? How does your service/product enhance your visitors’ /companies’ lives?
Then, through the eyes of your visitors, think about which search terms users should find you for. Consider that your visitors do not look for technical terms.
An ugly but substantial truth upfront: the best SEO in the world won’t improve a shitty product or low-quality content. In case you are unsure about your product or service — use your website to ask for feedback and learn from potential customers instead of reading this SEO guide.
After doing proper keyword research, my final result looked like this table. I used a google sheet to prioritize my keywords (feel free to duplicate the research template to your cloud):
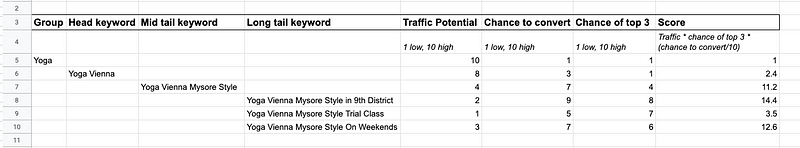
Here’s how I filled each column with content and how you can master your keyword research, too.
For the first four columns:
- Start with brainstorming all keywords that come to your mind and use the free tool “answer the public” for finding questions users ask related to your search term. Brainstorm at least four to five main groups for the first column.
- Find related keywords to your main groups based on google search with Yoast google suggest expander
- Look for keyword suggestions and keyword’s rank and search volume with ubersuggest by Neil Patel
- Compare the search volume for different keywords over time and region with Google Trends and fill in the column “traffic potential.” Note that this is no exact number, but your best guess.
As I had new websites with a domain authority lower than 5, I aimed for mid to long-tail keywords. A mid-tail keyword would be “Yoga Studio Vienna” and a long-tail keyword “Ashtanga Yoga Studio next to Vienna University.” Long-tail keywords contain 4–6 content words and are therefore more specific. You reach a more targeted audience, while the search volume (people that type this word combination into google) is lower.
“In SEO the keyword length matters because, at least in the beginning, we’re going to go after long tail keywords — very exact, intention-driven keywords with lower competition that we know can win, then gradually we’ll work our way to the shorter keywords .”
For me, focusing on long-tail keywords also made sense from the conversion potential. People who google “Yoga Vienna Mysore Style in 9th district” are more likely to become my customers than people who google “Yoga.”
You also notice in the excel file that I scored “chance for conversion” higher for long-tail keywords.
Lastly, make a good guess on your chance to rank in the top three.
Ranking in the top three means that google displays your site in the first three organic results for your specific keyword. Score your chance by researching what the three best ranking sites for your particular keywords are doing.
For ranking research, open an incognito window to research. With the tool “I search from,” you can access google from any location.
Do you have content that’s better than the current top 3? Do the current top 3 have a low domain authority? Great. This keyword is your chance to rank.
After you identified your top 5 keywords, check the competition that is ranking best for those keywords, and make better and more relevant content than they do. Here’s how.
Content Strategy and Content Creation
Before you determine a specific content topic, think about the search intent (=what are your visitors looking to find on your site).
Do your visitors want to buy something? Are your visitors looking for information? Do visitors come to your site for educational purposes? Each page you create should exist for one search intent.
Here’s what your website’s content pieces can do:
- you can demonstrate competence (case studies, industry updates, awards, lengthy testimonials from previous buyers)
- create consciousness about what you do (product pages, service descriptions)
- develop a sense of belonging (behind the scenes & team, company culture, philosophy on things)
Great! Once the search intent is clear, you can focus on creating content. If you already have ideas on content, you can skip the next paragraph as it shows you how to come up with content ideas.
As the Content Idea Generator, Google Analytics is a great tool. However, the best way is to ask your target audience about their interests.
You can also follow relevant hashtags on social media. Here are my favorite hacks for content creation:
- Find the content that performs best with buzzsumo
- Monitor new web content with Google Alerts
- Research the trending topics of the world with Google Trends
- Type in the first idea of your keyword and look at the sentences google suggests
Are you clear about the content you want to cover? Great, let’s continue with actually composing the content.
SEO Copywriting
Your blog posts are SEO Copywriting. I had to fail before realizing that SEO Copywriting is nothing similar to journaling or blogging.
In SEO Copywriting, your keywords come into life.
If you do not have the time (but the money) to outsource, take a look at SEO copywriters on Fiverr. I am a big fan of the YOAST plugin as it monitors your post’s quality and gives actionable advice on what to change.
Here is a checklist for single blog posts and SEO quality:
- Good readability — active voice, alternating sentence beginnings, transition words. For English texts, the free online writing assistant Grammarly can help.
- Keyphrase length — the optimum is up to 4 content words (e.g., Ashtanga Yoga Class in Vienna)
- Keyphrase in the slug, title, and subheadings — you should have your focus keyphrase of your article in your URL, in the <H1> title tag and your <H2> or <H3> tags
- The proper length of your piece — For a regular post it should be >300 words and for cornerstone content >900 words
- The adequate length and content of your meta description — between 120 and 156 characters with your key phrase in it, use an active voice with an actionable call to action
- Keyphrase density — 0.5%–3% is the optimal density, you can also include synonyms
- Images alt attribute — include your keyphrase in the image descriptions in your blog post
- Outbound and internal contextual links — your article should link to other relevant websites and also to other related sites on your page (follow or nofolllow). By building an internal linking structure, you show Google which of your pages are most important.
Before jumping to the (easier) part, one mistake I want you to prevent making: NEVER optimize different articles for one keyword. Otherwise, you are competing against yourself.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO improves your site in such a way that search engine spiders can crawl your website and index your content in their search results.
If you are already familiar with the terms “crawling, indexing and spiders” you can skip this 5-minute video.
The technical side is my favorite SEO part because you can work through a list step by step. In case you are wondering who determines the importance of each factor, take a look at Google’s search quality evaluator guidelines (Dec 2019).
If your time is better spent on other tasks and you have the financial resources, hire a Technical SEO freelancer on Fiverr. The following checklist can still help you determine which specific tasks to look for.
Page Speed Optimization
Page Speed matters. Check your current page speed with GTMetrix or with Googles Page Speed Insights.
Both metrics give you tailored advice on how to improve your page speed. The easy fix is the proper size of your web images (I reduced my image sizes with tiny png.)
As a rule of thumb, a picture should never exceed the size of 200kb. There are also plug-ins for image auto-optimization, but in my experience, the manual adjustment works better.
In addition to image optimization, use a caching plugin (I used and liked wp fastest cash).
On a side note: FB Pixel or Hotjar can make your page slower. Only enable both when you are testing and analyzing something. Otherwise, consider switching them off.
Mobile Optimization
The Google search algorithm strongly favors sites that are optimized for mobile devices. Most WordPress themes are mobile responsive.
Nevertheless, always make sure that the mobile content is displayed correctly.
For exploring your site’s mobile-friendliness, you can use the google chrome built-in testing tool to view your content from different devices. Here’s a video that explains how.
Repetitive Technical To Do’s on Your Site
- Use Tags for Hierarchy <H1> <H2> <H3> — only one H1 Tag per site (check source code on every single site)
- Use Meta Title Tags (e.g., check with this free tracker from SEObility where your site needs improvement).
- All URLs should be human-readable and contain keywords. Remove stopwords (such as “a” or “and”) from your permalinks.
- Alt descriptions of images. The alt description is the text that appears in place of an image on a webpage if the image fails to load on a user’s screen.
- Have clear path navigation visible on your site. Breadcrumbs show your visitors how the current page fits into the larger structure of your website and allow them to navigate. Moreover, Breadcrumbs allows google search to determine the structure of your site more easily. Add Breadcrumbs with the help of a Breadcrumb Plugin.
- HTTP Status Codes. Check for 404 errors in Google Search Console at Crawl errors. Google Search penalizes sites with many errors, as this can be a sign of bad maintenance. 301 redirects can help in solving this issue.
- Use Structured Data in your sites. Here’s an SEO’s guide to writing structured Data. Alternatively, Schema&Structured Data is a helpful plugin for WordPress Sites.
Crawlability
The crawlability determines whether search engine bots (like Google’s crawling spiders) can discover your site.
If your site is not crawlable, bots can not find it, and not list it in search results. Here’s how you make your sites crawlable and your On-Page SEO worth your work:
- Submit your XML.sitemap via the Google Search Console (Here’s how to submit it).
- Check whether your site has duplicate content that needs removal. If duplicate content is necessary, make use of canonical links and the robots.txt to avoid problems.
- robots.txt file tells search engine bots where they can or cannot visit your site. For example, you do not want your audience to find your checkout page in the search results. The official syntax of the robots tag is: <meta name=”robots” content =”value”> The most common robots value are index, noindex, follow and nofollow
Off-Page SEO
Off-Page SEO is everything you do away from your website that brings traffic to your site.
This part of SEO is about so-called “inbound links” from other websites to your site.
The higher the domain authority (=trustworthyness and relevance on the internet) of sites that refer to your site, the more valuable is such a link for you. Links from high authority domains to your site tell the search engine (e.g., Google) that you are referred to from trustworthy sources.
Let’s have a look at ways to gain those backlinks. In contrast to Technical SEO, (whitehat) backlink building requires continuous long-term work.
Backlink strategy
There are several paths that you can include in your backlink strategy:
- Google alert for your company name and always claim to mention your enterprise’s name + a link to your site
- Google your keyword inurl:blog intext”learn more” to figure out blogs you can address
- look for old content in your niche, make it better and send it to all sites that currently have old backlinks
- For a high domain authority page link, you can contact your last education institute and suggest writing a blog post for them. For example, I composed a blog entry for Vienna Business University on “Do you need to study if you want to found your company?”
Public Relations
Press coverage can help to gain more traffic from external sources. I followed these steps to gain traction from newspapers:
- Build a Public Relations network by attending journalism meetups and talking to journalists at conferences.
- Draft a story and send it to contacts you met and general newspapers.
- Prepare a media kit with the image sizes and company description length required for your newspaper.
Sounds too easy? This step is all about trial and error, story, and timing.
The more you try, the likelier the chances that a newspaper will cover your topic and refer to you. Are there any trade journals in your niche that would benefit from your insights?
Is there any local newspaper in the area you grew up that would want to portrait you? These are good questions to start with.
Conclusion
For successful SEO, the three fields of Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and Off-Page SEO are equally important.
Your time is limited. Decide how much time you dedicate to each SEO field and you want to outsource specific parts like SEO Copywriting or Technical SEO.
SEO is a never-ending process. If you’ll ever say “I have done it all, and I’m finished with SEO,” — you did not understand SEO at all.
Even a few hours of serious SEO work can move the crawl spiders to index your page.
Do you want to stay in touch? Join my E-Mail List.